First Class Info About How To Treat Subclinical Hypothyroidism

This guideline was triggered by a recent systematic review of randomised controlled trials, which could alter practice.
How to treat subclinical hypothyroidism. On completion of this article you should be able to: However, individuals with cardiovascular risk and subclinical hypothyroidism may benefit from levothyroxine treatment. Because patients with subclinical hypothyroidism sometimes have subtle hypothyroid symptoms and may have mild abnormalities of serum lipoproteins and cardiac function, patients with definite.
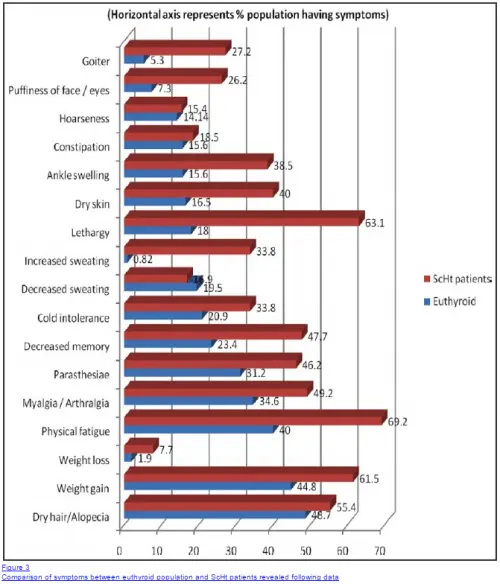
Because it doesn't cause any symptoms, subclinical hypothyroidism isn't noticeable. This article explores subclinical hypothyroidism, including the causes,. 1,2 it is sometimes referred to as mild hypothyroidism or borderline hypothyroidism and is often linked with autoimmune thyroid disease (hashimoto’s disease).
For a mild rise in tsh , thyroid hormone medicine may not be useful. Subclinical hypothyroidism is present in 3.7% of the u.s. Free t3, free t4 and reverse t3 levels should be evaluated to determine peripheral conversion status.
1 unlike overt hypothyroidism, which is treated with levothyroxine for symptomatic relief and cardiovascular disease (cvd) risk reduction, the treatment recommendations for subclinical hypothyroidism remain controvers. However, providers may recommend treatment in the following cases: If your tsh level is higher, but still in the subclinical range, thyroid hormones may improve some symptoms.
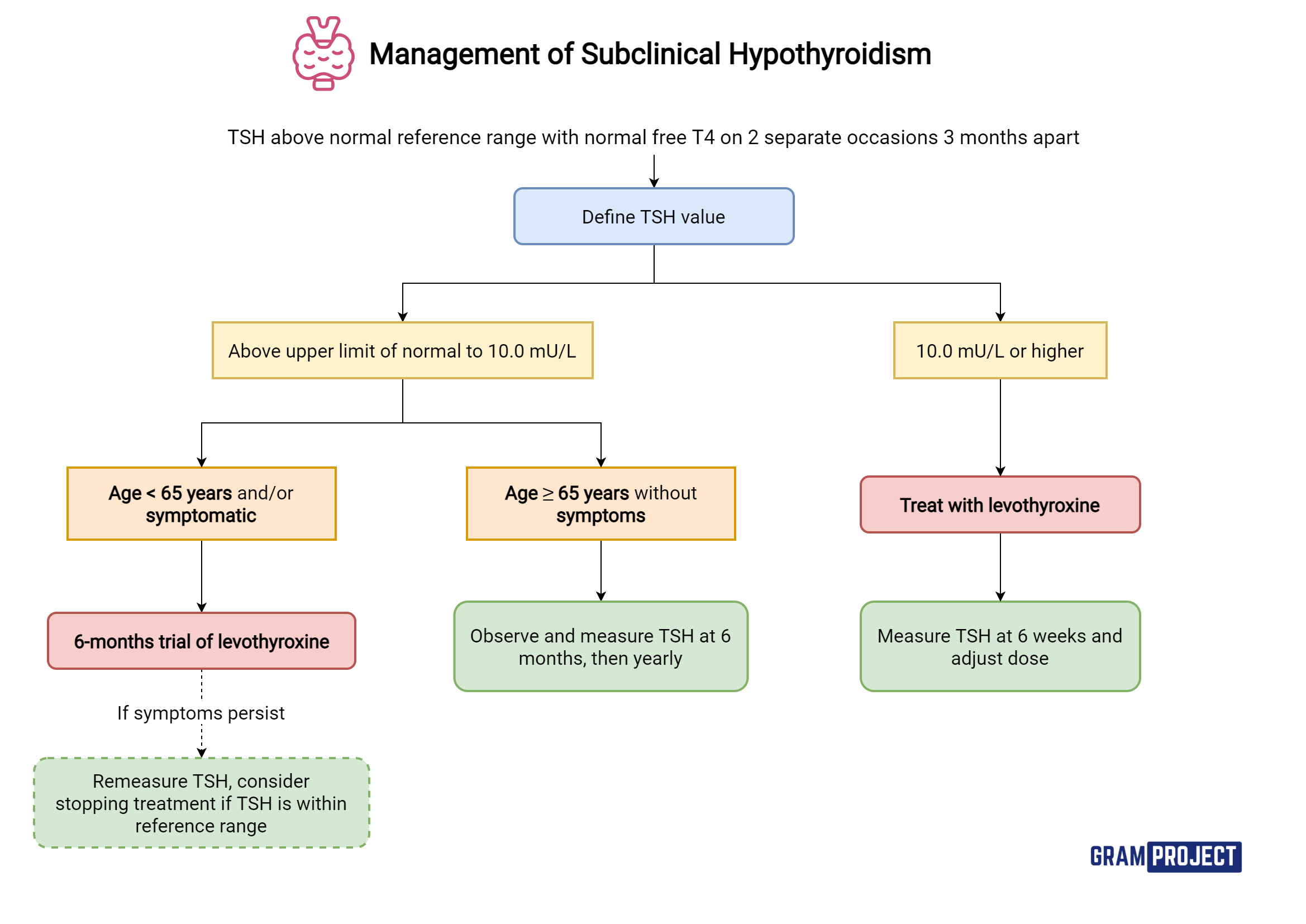
Measure free thyroxine (ft4) if the patient’s tsh is above the reference range. This usually makes the symptoms disappear completely. Whether it should be treated remains controversial.
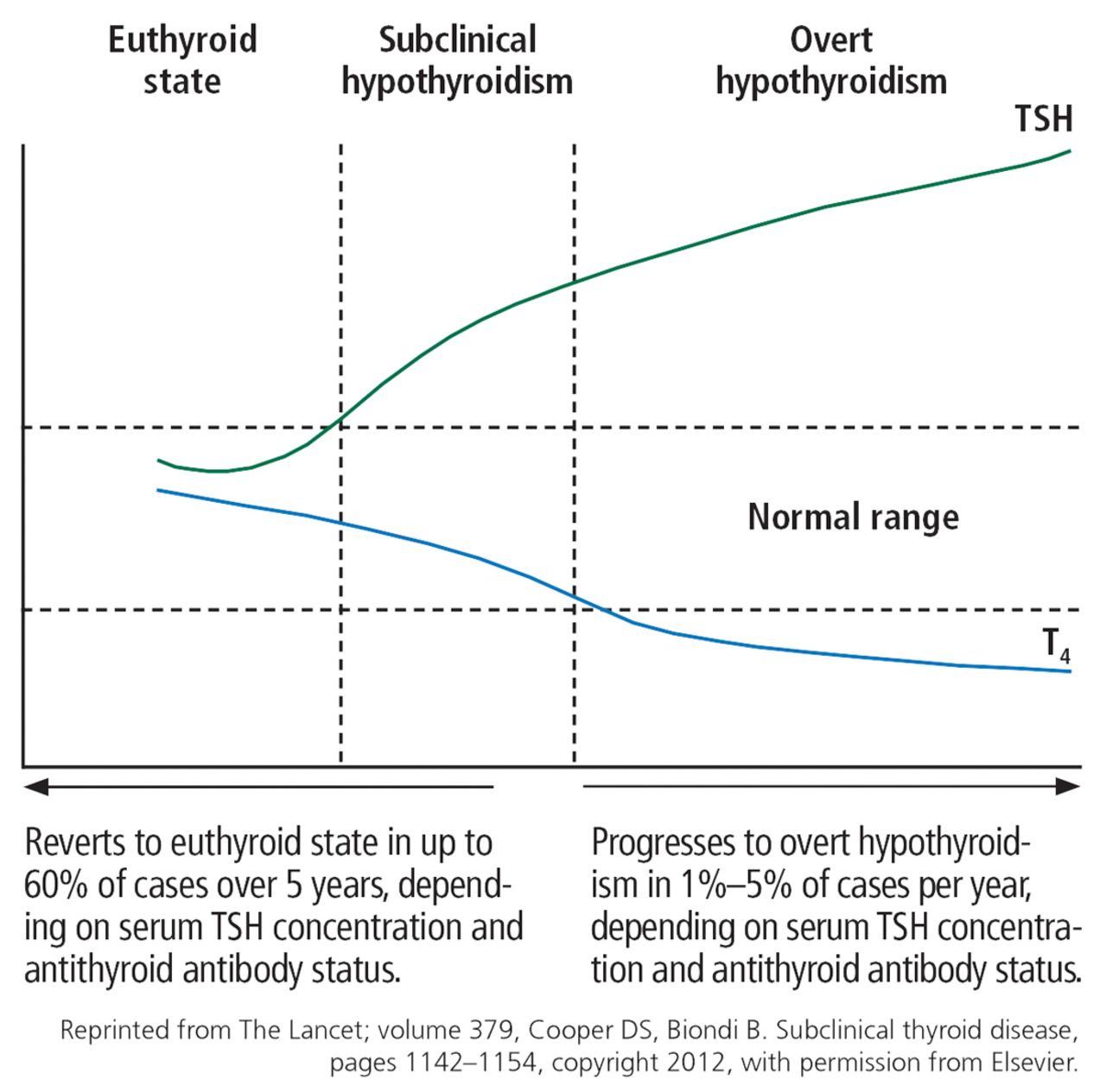
This finding should initiate a tpo antibody test and an additional tsh test in six to 12 months. About 90% of all patients with sch have tsh levels between 4 and 10 miu/l (3, 4).sch. Has a goitre, nodule, or structural change in the thyroid gland.
Treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism may include the thyroid hormone replacement medication levothyroxine. Whether it should be treated remains controversial.
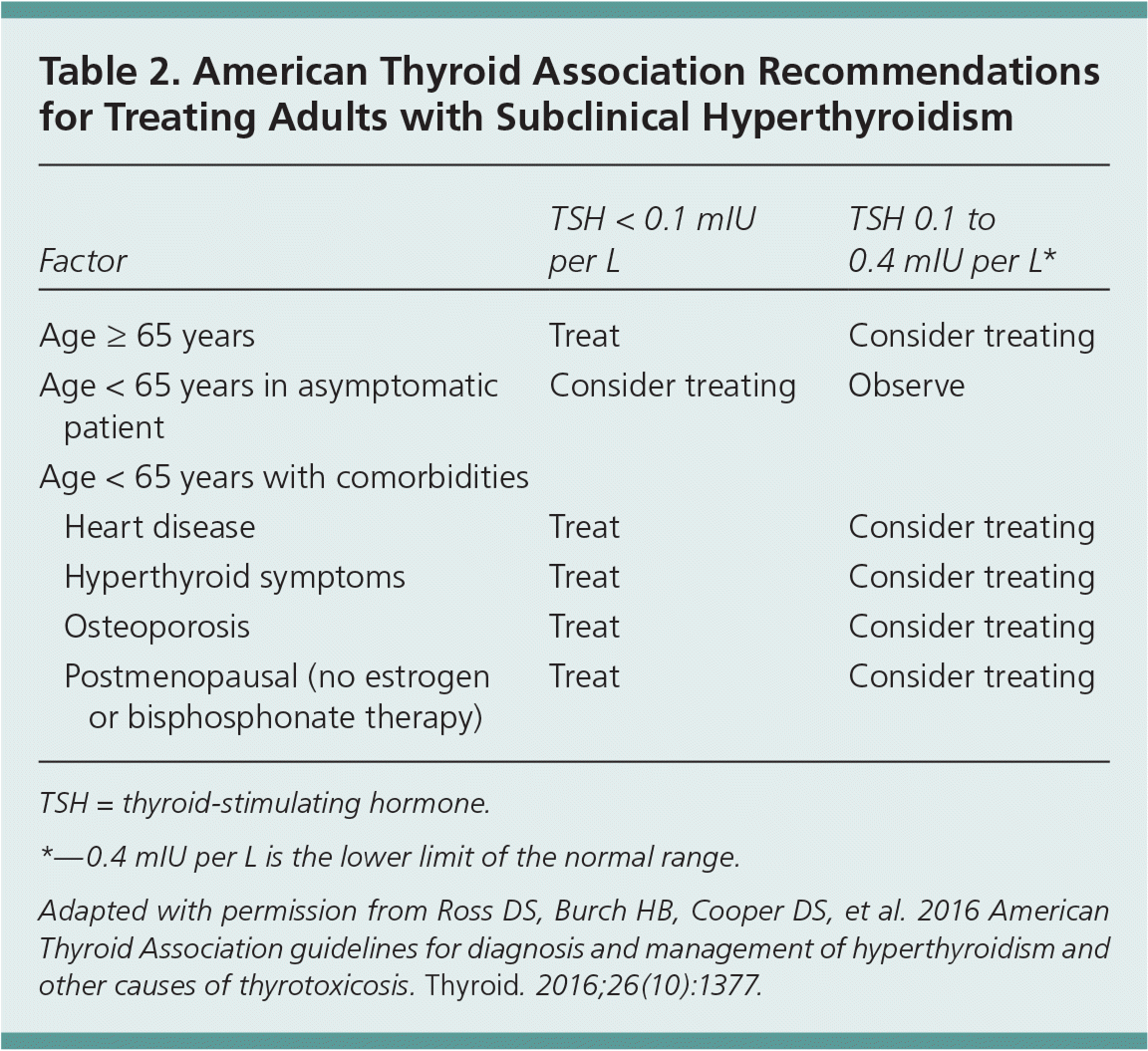
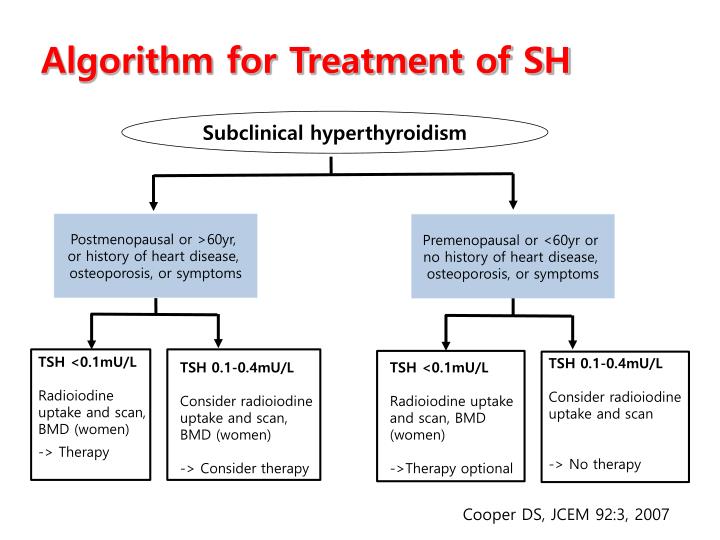
In subclinical hypothyroidism with tsh >10 miu/l, treatment is indicated. Another study presented high frequency of subclinical hypothyroidism: Subclinical hypothyroidism is categorised as tsh levels above the range but with normal levels of thyroxine (t4) and triiodothyronine (t3).
Hypothyroidism can be treated easily by taking a tablet containing the thyroid hormone once a day. These tablets act to replace the thyroxine that is not being produced. Currently, the best practical approach is to base treatment decisions on the degree of tsh elevation, thyroid autoimmunity, and.
There’s no good scientific evidence that eating or not eating certain foods will definitely help to stave off subclinical hypothyroidism or treat it if you’ve already been diagnosed. For most people with subclinical hypothyroidism, providers recommend that they take a “wait and see” approach and not start treatment to see if the subclinical hypothyroidism resolves on its own. (1) diagnose and interpret the meaning and clinical importance of subclinical hypothyroidism, (2) assess possible adverse effects of mild thyroid failure and describe the current knowledge about the effect of levothyroxine therapy in mild thyroid failure, and (3) select patients with.